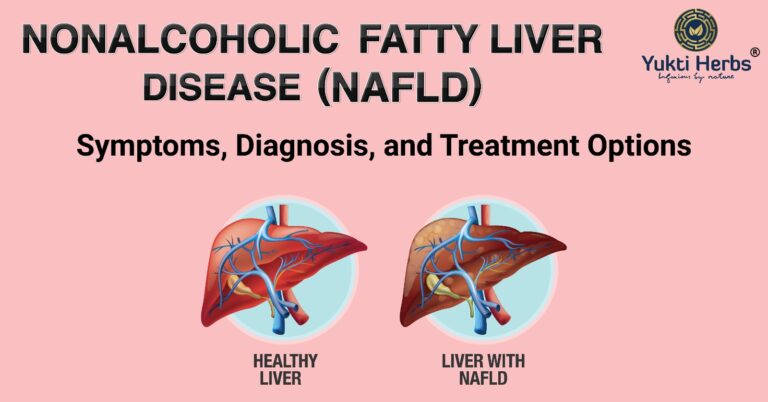
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver cells, without any alcohol consumption. It is becoming increasingly prevalent in Western societies, with an estimated 25% of the world’s population affected. While the condition is usually benign, it can progress to liver damage, inflammation, and scarring in some cases. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for NAFLD.
Symptoms of NAFLD:
NAFLD is often asymptomatic, meaning that many people may not experience any symptoms. However, in some cases, people may experience fatigue, abdominal discomfort, or a general feeling of being unwell. When the condition progresses to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), patients may experience symptoms such as jaundice, itching, and swelling in the legs and abdomen.
Diagnosis of NAFLD:
The diagnosis of NAFLD is typically made through blood tests, imaging studies, and a liver biopsy. Blood tests will show increased levels of liver enzymes and other markers of liver damage. Imaging studies such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect the buildup of fat in the liver. A liver biopsy is the most definitive way to diagnose NAFLD and can determine the extent of liver damage.
Treatment options for NAFLD:
- Lifestyle changes: The first line of treatment for NAFLD is lifestyle changes. Weight loss, healthy eating, and regular exercise are recommended for patients with NAFLD. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can significantly reduce liver fat content and improve liver function. A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help reduce inflammation and improve liver health. Patients should also avoid foods that are high in saturated fats, added sugars, and salt.
- Medications: There are currently no approved medications for the treatment of NAFLD. However, some medications may be used off-label to treat certain aspects of the disease. For example, drugs that lower blood glucose levels, control cholesterol levels or reduce triglycerides may be prescribed. These medications should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended for the treatment of NAFLD. Bariatric surgery, which involves the reduction of the size of the stomach, can help patients lose significant amounts of weight and improve liver function. Liver transplant is also an option for patients with advanced liver disease.
Prevention of NAFLD:
Prevention is key when it comes to NAFLD. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can all help prevent the development of NAFLD.
In conclusion, NAFLD is a common condition that can progress to liver damage, inflammation, and scarring. Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests, imaging studies, and a liver biopsy. NAFLD Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery. Prevention is key when it comes to NAFLD, and maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can all help prevent the development of NAFLD.
References:
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease – Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease – American Liver Foundation. https://liverfoundation.org/for-patients/about-the-liver/diseases-of-the-liver/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/










[…] NAFLD where fat accumulates in the liver cells, without any alcohol consumption. Checkout NAFLD Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Ayurvedic Treatment […]